钢琴曲及流行音乐和弦谱
展开阅读
展开阅读
格式说明:1234567表示和弦级数,“,”分隔不同小节,“ ”分隔同一小节和弦,M表示大和弦,m表示小和弦,其余符号标记在括号内,如IVm7-5表示为4m(7-5),但顺阶和弦的大小不会标出。歌曲名字下标记出调式(不严格按照原歌曲调式)
誰かが傷ついても
bB大调(其实是g小调,懒得改了)
6,4,2 5,1
4,2,7,3
4,5,6 5,4
2,6,2,3M
6,3,4 5,1
4,3,2,3M
6,3,4 5,1
4,3,2 5,6,2 5,4,6
綺麗で儚いもの
#F大调
1 3,6,5 4,1 5
1 3,6,1 2,4 5
6 5,4,6 5,4
2 5,3 6,4
1(add9),5
4,1,2 b6,6,4,1,2,5
4,1,2 b6,6,4 5,3 6,2 5,1
展开阅读
在计算反向传播或最优化问题时,经常遇到向量、矩阵、张量对向量、矩阵、张量的求导问题,而类比普通函数求导经常无法处理矩阵转置的问题,因此需要使用一套更简单的符号系统进行运算,即里奇微积分。
相乘时符号相同且共轭的指标,如一个共变自由指标(下标)遇到一个符号相同的反变自由指标(上标),会发生缩并运算成为哑指标,整个表达式自由指标的个数表示最终结果的自由指标个数;当自由指标只有一个 $i$ (如 $x^i,A_i^jx^i=y^j$ )时,表达式是一个向量(一维张量),有两个 $i,j$ (如 $A_i^j,A^{ij},A_i^jx^j$ )时,表达式是一个二维张量,以此类推。
$R^n$ 表示n维列向量空间, $R^{n*}$ 表示n维行向量空间,$A_{ij}$ 表示双线性映射 $R^n\times R^n\rightarrow R$ , $A^{ij}$ 表示双线性映射 $R^{n*}\times R^{n*}\rightarrow R$,$x^i$ 表示列向量 $x$, $x_i$ 表示行向量$x^T$(也叫线性泛函或余向量)。
$\delta_i^j$ 是一个单位矩阵, $\delta_{ij}$ 是度量张量(一个双线性映射), $\delta^{ij}$ 是共轭度量张量,它们有这些性质:$x^j(=x)$ 表示原向量则$\delta_{ij}x^j=x_i(=x^{\top})$ 表示转置向量, $\delta^i_jx^i=\operatorname{diag}(x)$ , $A_j^i(=A)$ 表示原矩阵则$\delta_{ii}\delta^{jj}A_j^i(=A^\top)$ 表示转置矩阵, $\delta_{ii}\delta^{ii}=1$ , $\delta_{ij}\delta^{ii}=\delta_j^i$ ,$\frac{dx_i}{dx^j}=\delta_i^j$ , $\frac{dx^i}{dx^j}=\delta^{ij}$ , $\frac{dx_i}{dx_j}=\delta_{ij}$ , $\frac{d X_i^j}{d X_k^l} = \delta^{jl}\delta_{ik}$
$c = x ^ { \top } y \quad c = x _ { i } y ^ { i }$
$x = A y \quad x ^ { i } = A _ { j } ^ { i } y ^ { j }$
$x ^ { \top } = y ^ { \top } A \quad x _ { j } = y _ { i } A _ { j } ^ { i }$
$C = A \cdot B \quad C _ { k } ^ { i } = A _ { j } ^ { i } B _ { k } ^ { j }$
$A = x y ^ { \top } \quad A _ { j } ^ { i } = x ^ { i } y _ { j }$
$z = x \odot y \quad z ^ { i } = x ^ { i } y ^ { i }$
$A=x\otimes y \quad A^{ij}=x^i y^j$
$C=A\otimes B\quad C^{ij}_{kl}=A_k^i B_l^j$
$B=A\otimes x\quad B_{ij}^k=A_{ij}x^k$
$B = A \operatorname { diag } ( x ) \quad B _ { j } ^ { i } = A _ { j } ^ { i } x _ { j }$
$B = \operatorname { diag } ( x ) A \quad B _ { j } ^ { i } = x ^ { i } A _ { j } ^ { i }$
根据上述原理计算 $x^TAx$ 对 $x$ 的导数:
$\frac{d (x^{\top}Ax)}{dx}$
$=\frac{d (x_i A_j^i x^j)}{d x^k}$
$=\frac{d x_i}{d x^k}A_j^i x^j+x_i A_j^i \frac{d x^j}{d x^k}$
$=\delta_i^k A_j^i x^j+ x_i A_j^i \delta^{jk}$
$=A_j^k x^j+x_i A_j^i \delta^{jk} \delta_{kk} \delta^{kk}$
$=A_j^k x^j+x_i A_j^i \delta^{j}_k \delta^{kk}$
$=A_j^k x^j+x_i A_k^i \delta^{kk}$
$=A_j^k x^j+\delta_{ii}x^i A_k^i \delta^{kk}$
$=Ax+A^{\top}x$
计算 $y\odot (Xw)$ 对 $X$ 的导数:
$\frac{\partial (y\odot (Xw))}{\partial X}$
$=\frac{\partial (y^i X_j^iw^j)}{\partial X_k^l}$
$=y^i\delta^{il}\delta_{jk}w^j$
$=y^i\delta^{il}w_k$
$=\operatorname{diag}(y)\otimes w^\top$
需要注意的是, $\delta_{ii}$ 和 $\delta^{ii}$ 并不像常规的Kronecker符号一样等于n(n是下标对应的维数),而是满足$\delta_{ii}\delta^{ii}=1$ ,它有特殊的用途。在本文中,它主要用于表示矩阵转置。在爱因斯坦约定中,表示矩阵转置是一个容易引起记号混乱的事,如果使用 $A_i^j$ 表示原矩阵(方阵), $A_j^i$ 表示转置矩阵,那么原本 $A_i^j x^i=y^j$ ,转置后却因为指标无法缩并而无法相乘得到列向量了: $A_j^i ? x^i$ ;此外,不区分上下标的爱因斯坦约定对于这是匪夷所思的。但是根据上面的定义,可以使用 $A_j^i \delta_{ii}\delta^{jj}x^i$ 表示 $A^\top x$ ,而不会产生歧义。事实上,在爱因斯坦约定中,指标只能用于表示张量的各个维,如果张量是对称的,那么不管怎么排列指标,表达式看起来都是一样的,因此本文的参考文献[4]使用了上述 $\delta_{ii}$ 和 $\delta^{ii}$ 符号规避了此问题。
如果你没有看懂本文,没有关系,使用参考文献[4]对应的网站http://matrixcalculus.org/即可在线计算矩阵、张量求导。即使你不懂如何计算爱因斯坦约定,你也可以通过numpy的np.einsum()来帮助你计算爱因斯坦约定,更多有关爱因斯坦约定的内容请参考[10]。
在tensorflow中使用爱因斯坦求和约定可以极大的简化代码,使用以下代码实现矩阵乘法:
$R=A B\quad R_i^k=A_i^j B_j^k$
import tensorflow as tf
R = tf.einsum('ij,jk->ik',A,B)参考文献
[1] Matrix calculus - Wikipedia
[2] Ricci calculus - Wikipedia
[3] Kronecker delta - Wikipedia
[4] S. Laue, M. Mitterreiter, and J. Giesen. Computing Higher Order Derivatives of Matrix and Tensor Expressions, NIPS 2018.
展开阅读

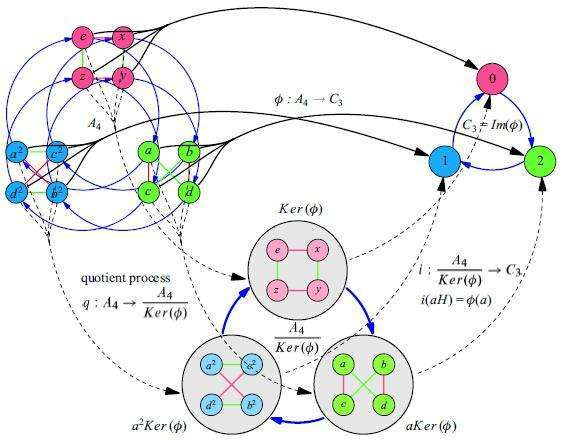
G是群, $a\in G$ 则 $|a|$ 表示a的阶
$a|b$ 表示a整除b,如2|6
$a\perp b$ 表示a和b互素,如 $3\perp 5$
d是r和s的最小公倍数记作 $d=[r,s]$
群G有子群H,群G的阶是可以被子群H的阶整除的,此时我们称[G:H]为H在G下的指数,指数的多少与陪集个数是相同的
对于环)(R,+,·),已知(R, +)是阿贝尔群。R的子集I称为R的一个右理想,若I满足:
如果I既是R的右理想又是R的左理想,那么I是R的理想。
设G是群,H是G的子群,称子群H在群G中的左陪集或右陪集的个数为H在G中的指数,记作 $\left[ {G:H} \right]$ 。拉格朗日定理: $|G| = |H|\left[ {G:H} \right]$
设H是群G的子群,如果对每个 $a\in G$ 都有 $aH=Ha$ 则称H是群G的正规子群,记作 $H \triangleleft G$ ,如果G只有平凡的正规子群,且 $G\neq \{e\}$ 则称G为单群
设G为群,H是G的正规子群,H的所有陪集 $G/H = \{ aH|a \in G\} $ 关于G的子集上的乘法运算构成的群称为G关于H的的商群
环R的理想 P是素理想,当且仅当它是一个真理想(也就是说,P ≠ R),且对于R的任何两个理想A和B,若有AB ⊆ P,则A ⊆ P或B ⊆ P。
任意有单位元的环一定有极大理想,a是R的极大理想当且仅当R/a是单纯环
除环 非零环 整环
展开阅读
import numpy as np
import cv2
def zmMinFilterGray(src, r=7):
'''最小值滤波,r是滤波器半径'''
return cv2.erode(src, np.ones((2*r+1, 2*r+1)))
def guidedfilter(I, p, r, eps):
'''引导滤波,直接参考网上的matlab代码'''
height, width = I.shape
m_I = cv2.boxFilter(I, -1, (r,r))
m_p = cv2.boxFilter(p, -1, (r,r))
m_Ip = cv2.boxFilter(I*p, -1, (r,r))
cov_Ip = m_Ip-m_I*m_p
m_II = cv2.boxFilter(I*I, -1, (r,r))
var_I = m_II-m_I*m_I
a = cov_Ip/(var_I+eps)
b = m_p-a*m_I
m_a = cv2.boxFilter(a, -1, (r,r))
m_b = cv2.boxFilter(b, -1, (r,r))
return m_a*I+m_b
def getV1(m, r, eps, w, maxV1): #输入rgb图像,值范围[0,1]
'''计算大气遮罩(暗通道)图像V1和光照值A, V1 = 1-t/A'''
V1 = np.min(m,2) #得到暗通道图像
#V1 = inverse_color_01(V1)
# cv2.imshow("dark channel", V1)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
V1 =guidedfilter(V1, zmMinFilterGray(V1,7), r, eps) #使用引导滤波优化
bins = 2000
ht = np.histogram(V1, bins) #计算大气光照A
d = np.cumsum(ht[0])/float(V1.size)
for lmax in range(bins-1, 0, -1):
if d[lmax]<=0.999:
break
A = np.mean(m,2)[V1>=ht[1][lmax]].max()
V1 = np.minimum(V1*w, maxV1) #对值范围进行限制
return V1,A
def deHaze(m, r=81, eps=0.001, w=0.95, maxV1=0.80):
Y = np.zeros(m.shape)
V1,A = getV1(m, r, eps, w, maxV1) #得到遮罩图像和大气光照
for k in range(3):
Y[:,:,k] = (m[:,:,k]-V1)/(1-V1/A) #颜色校正
Y = np.clip(Y, 0, 1)
return Y
def interpo(x, middle_ratio, max_x, max_num):
# 自定义的直方图
#| /\
#| / \
#| / \
#|/____ratio___\___
#
if not 0<=x<=max_x:
return 0
elif x<middle_ratio*max_x:
return int(max_num/(middle_ratio*max_x)*x)+1
else:
return int(max_num - max_num/(255-middle_ratio*max_x)*(x-middle_ratio*max_x))+1
def func(ratio):
# 使用自定义的直方图曲线func()生成直方图实例化图像
ret = []
for i in range(256):
ret = ret + [i]*interpo(i, ratio, 255, 1000)
return np.array(ret)
def find_nearest_above(my_array, target):
diff = my_array - target
mask = np.ma.less_equal(diff, -1)
# We need to mask the negative differences
# since we are looking for values above
if np.all(mask):
c = np.abs(diff).argmin()
return c # returns min index of the nearest if target is greater than any value
masked_diff = np.ma.masked_array(diff, mask)
return masked_diff.argmin()
def hist_match(original, specified):
oldshape = original.shape
original = original.ravel()
specified = specified.ravel()
# get the set of unique pixel values and their corresponding indices and counts
s_values, bin_idx, s_counts = np.unique(original, return_inverse=True,return_counts=True)
t_values, t_counts = np.unique(specified, return_counts=True)
# Calculate s_k for original image
s_quantiles = np.cumsum(s_counts).astype(np.float64)
s_quantiles /= s_quantiles[-1]
# Calculate s_k for specified image
t_quantiles = np.cumsum(t_counts).astype(np.float64)
t_quantiles /= t_quantiles[-1]
# Round the values
sour = np.around(s_quantiles*255)
temp = np.around(t_quantiles*255)
# Map the rounded values
b=[]
for data in sour[:]:
b.append(find_nearest_above(temp,data))
b= np.array(b,dtype='uint8')
return b[bin_idx].reshape(oldshape)
def hist_match_all(img):
# 对图像的每个通道都进行直方图规定化,使用func()中定义的直方图进行规定
result = np.zeros_like(img)
for i in range(3):
specified = func(0.2)
result[:,:,i] = hist_match(img[:,:,i], specified)
return result
def image_hist(image): #画三通道图像的直方图
color = ("blue", "green", "red")#画笔颜色的值可以为大写或小写或只写首字母或大小写混合
for i, color in enumerate(color):
hist = cv2.calcHist([image], [i], None, [256], [0, 256])
plt.plot(hist, color=color)
plt.xlim([0, 256])
plt.show()
def normalize(img):
# 将像素最大值小于255的图像归一化到255
return (img/np.max(img)*255).astype(np.uint8)
def hist_match_dark_prior(img, dark=False):
# 基于暗/亮通道的直方图规定化
result = img.copy()
for i in range(3):
result[:,:,i] = cv2.equalizeHist(result[:,:,i])
if dark==False:
dark_prior = np.min(result, axis=2)
else:
dark_prior = np.max(result, axis=2)
#image_hist(np.stack([dark_prior]*3, axis=2))
for j in range(3):
for i in range(3):
result[:,:,i] = hist_match(result[:,:,i], dark_prior)
result = normalize(result)
#image_hist(result)
return result
if __name__=="__main__":
img = cv2.imread("filename")
img = hist_match_all(img)
img = dehaze255(img)
cv2.imwrite("filename_write", img)再放一个pytorch版的:
import torch
def torch_equalize(image):
"""Implements Equalize function from PIL using PyTorch ops based on:
https://github.com/tensorflow/tpu/blob/master/models/official/efficientnet/autoaugment.py#L352"""
def scale_channel(im, c):
"""Scale the data in the channel to implement equalize."""
im = im[:, :, c]
# Compute the histogram of the image channel.
histo = torch.histc(im, bins=256, min=0, max=255)#.type(torch.int32)
# For the purposes of computing the step, filter out the nonzeros.
nonzero_histo = torch.reshape(histo[histo != 0], [-1])
step = (torch.sum(nonzero_histo) - nonzero_histo[-1]) // 255
def build_lut(histo, step):
# Compute the cumulative sum, shifting by step // 2
# and then normalization by step.
lut = (torch.cumsum(histo, 0) + (step // 2)) // step
# Shift lut, prepending with 0.
lut = torch.cat([torch.zeros(1), lut[:-1]])
# Clip the counts to be in range. This is done
# in the C code for image.point.
return torch.clamp(lut, 0, 255)
# If step is zero, return the original image. Otherwise, build
# lut from the full histogram and step and then index from it.
if step == 0:
result = im
else:
# can't index using 2d index. Have to flatten and then reshape
result = torch.gather(build_lut(histo, step), 0, im.flatten().long())
result = result.reshape_as(im)
return result.type(torch.uint8)
# Assumes RGB for now. Scales each channel independently
# and then stacks the result.
image = image.type(torch.float)
s1 = scale_channel(image, 0)
s2 = scale_channel(image, 1)
s3 = scale_channel(image, 2)
image = torch.stack([s1, s2, s3], 2)
return image
def find_nearest_above(my_array, target):
diff = my_array - target
mask = diff <= -1
# We need to mask the negative differences
# since we are looking for values above
if torch.all(mask):
c = torch.abs(diff).argmin()
return c # returns min index of the nearest if target is greater than any value
masked_diff = diff.clone()
masked_diff[mask] = 9999
return masked_diff.argmin()
def hist_match(source, template):
s = source.view(-1)
t = template.view(-1)
s_values, bin_idx, s_counts = torch.unique(s, return_inverse=True, return_counts=True)
t_values, t_counts = torch.unique(t, return_counts=True)
s_quantities = torch.cumsum(s_counts,0).type(torch.float)
t_quantities = torch.cumsum(t_counts,0).type(torch.float)
s_quantities = s_quantities/s_quantities[s_quantities.shape[0]-1]
t_quantities = t_quantities/t_quantities[t_quantities.shape[0]-1]
sour = (s_quantities * 255).type(torch.long)
temp = (t_quantities * 255).type(torch.long)
b = torch.zeros(sour.shape)
for i in range(sour.shape[0]):
b[i] = find_nearest_above(temp, sour[i])
s=b[bin_idx]
return s.view(source.shape)
def hist_match_dark_prior(img):
# input: img[h, w, c]
# output:res[h, w, c]
result = img.clone()
result = torch_equalize(result)
dark_prior,_ = torch.min(result, axis=2)
for i in range(3):
result[:,:,i] = hist_match(result[:,:,i], dark_prior)
return result
if __name__=='__main__':
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
im=Image.open("Night-schene-03.jpg")
img=torch.from_numpy(np.array(im))
img1=hist_match_dark_prior(img).numpy()
im1=Image.fromarray(img1)
im1.save('out.png')展开阅读
库拉托夫斯基闭包公理可来定义一个集上的拓扑结构,它和以开集作定义拓扑结构的公理等价:
拓扑空间 $(X,\mathrm{cl})$ 是集合X及作用在X的幂集上的闭包算子 $\mathrm{cl}:\mathcal{P}(X)\rightarrow \mathcal{P}(X)$ 且满足以下条件:
A是闭集,如果 $A=\mathrm{cl}(A)$
开集:所有点都是内点,至多可数个开集的并
闭集:开集的余
德语中使用G表示开,F表示闭,δ 表示交,σ表示并
因此Fδ集是闭集的交(有理数集就是一个Fδ集),开集都是Fσ集,闭集都是Gδ集
$\mathcal{B}(X,Y)$ 表示从赋范线性空间X到Y的有界线性算子集。若Y是Banach空间(完备赋范线性空间),则 $\mathcal{B}(X,Y)$ 是Banach空间
展开阅读
如果使用agencement de clavier «français»和modèle du clavier macintosh的话,还是可以打出来«和»的,键盘布局图如下
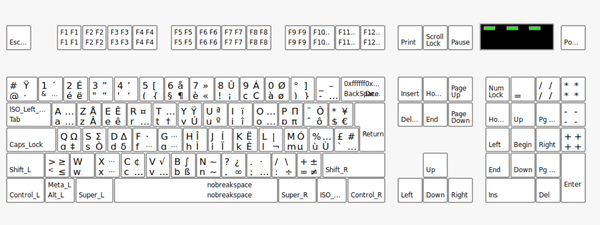
微软自带的键盘布局太垃圾了,连«和»都打不出来。这个键盘布局应该是最适合英语键盘用户的法语键盘布局了。windows用户直接点最下方Installation中的zip archive链接下载就可以。以下是键盘布局:

来法国才一个星期,我就遇到了各种各样的难题,法语键盘是其中之一。昨天费了很大力气,终于搞定了从QWERTY键盘到AZERTY(法语)键盘的映射表:
使用win10自带的法语(法国)法语键盘
格式:[fr] -> [en]
a <-> q
z <-> w
m -> ;
, -> m
. -> <
: -> .
( -> 5
) -> -
{ -> 右Alt + 4
} -> 右Alt + =
[ -> 右Alt + 5
] -> 右Alt + -
- -> 6
* -> \
? -> M
' -> 4
" -> 3
! -> /
/ -> >
% -> "
² -> `
° -> _
@ -> 右Alt + 0
-> 右Alt + 8
# -> 右Alt + 3
| -> 右Alt + 6
^ -> 右Alt + [
é -> 2
è -> 7
à -> 0
ù -> '
ç -> 9
â -> 按[再按a
ä -> 按{再按a
ã -> 右Alt+2 再按 a
à -> 右Alt+7 再按 a
法语键盘上不存在的字符:
< -> Alt + 60
> -> Alt + 62
« -> Alt+ 171
» -> Alt+ 187
展开阅读
[ə]:e [œ/O]:e紧张 [ø/X]:e/ei
[e]:ei
[ɔ/R]:ao
[o]:ou
[y]:ü [ɥ/H]:ü紧张
[ε]:ai
[œ̃]:an
[ɑ̃/D]:ang
[ᴐ̃ /S]:ong
[ɲ/M]:nie
[ε̃ /Y]:ang
[ʃ/F]
[ӡ/V]
## 几种常见的词素及发音
(元)y(元):ii
oi:[wa]
ien:[jε̃ ]
oin:[wε̃ ]
辅ill:[ij]
tion:[tjᴐ̃ ] [sjᴐ̃ ]
sion:[sjᴐ̃ ] 元[zjᴐ̃ ]
à:[a]
è,ê,ei,ai,aî,词尾et,词首e(x):[ε]
î,y:[i]
où,oû:[u]
qu:[k]
ç,x:[s]
e词末,e词首,辅辅e辅:[ə]
eu,œu:[œ]
ou元:[w]
ch:[ʃ]
j,ge,gi,gy:[ӡ]
é,er,ez词尾,es单音:[e]
o,au(r):[ɔ]
w:[v]
ô,au,eau:[o]
un,um:[œ̃]
û,u:[y]
an,am,en,em:[ɑ̃]
on,om:[ᴐ̃ ]
u元:[ɥ]
gn:[ɲ]
in:[ε̃ ]开音符(accent grave):è口型较大
闭音符(accent aigu):é口型较小
长音符(accent circonflexe):ô时间较长
分音符(tréma):ë与前面元音分开
软音符(crédille):ç将k发s音
单数
主语
je tu il/elle/on(他 她 他/她);
主有形容词(阳/阴/复)
mon/ma/mes ton/ta/tes son/sa/ses; 自反me te se
重读人称代词 直接宾语(COD) 间接宾语(COI)
moi toi lui/elle me te le/la en me te lui
复数
主语
nous vous ils/elles;
主有形容词(阳/阴/复)
notre/./nos votre/./vos leur/./leurs;自反nous vous se
重读人称代词 直接宾语(COD) 间接宾语(COI)
nous vous eux/elles nous vous les en nous vous leur
n.m.阳性名词
n.f.阴性名词
n.pl.复数名词
v.t.及物动词
v.i.不及物动词
v.pr.代词式动词
adj.dém.指示形容词
art.冠词
adj.poss.主有形容词
adj.indéf.泛指形容词
adj.interr.疑问形容词
pron.pers.人称代词
pron.rel.关系代词
pron.interrog.疑问代词
pron.dém.指示代词
adv.副词
prép介词
conj.连词
interj.叹词
det.(deterniner)限定词1. le (det.) the; (pron.) him, her, it, them
2. de (det.) some, any; (prep.) of, from
3. un (det.) a, an; (adj., pron.) one
4. à (prep.) to, at, in
5. être (verb) to be; (noun [m.]) being
6. et (conj.) and
7. en (prep.) in, by; (adv., pron.)
8. avoir (verb) to have; (noun [m.]) assets
9. que (adv., pron., conj.) that, which, who, whom
10. pour (prep.) for, in order to
11. dans (prep.) in, into, from
12. ce (det., pron.) this, that
13. il (pron.) he, it
14. qui (pron.) who, whom
15. ne (adv.) not
16. sur (prep.) on, upon; (adj.) sour
17. se (pron.) oneself, himself, herself, itself, themselves
18. pas (adv.) not; (noun [m.]) footstep
19. plus (adv.) more, no more
20. pouvoir (verb) to be able to, can; (noun [m.]) power
21. par (prep.) by
22. je (pron.) I
23. avec (prep.) with
24. tout (adj., adv., pron., det.) all, very
25. faire (verb) to do, make
26. son (det.) his, her its; (noun [m.]) sound; bran
27. mettre (verb) to put, place
28. autre (det., pron.) other
29. on (pron.) one, we
30. mais (conj., adv.) but
31. nous (pron.) we, us
32. comme (conj., adv.) like, as
33. ou (conj.) or
34. si (conj.) if, whether; (adv.) so
35. leur (det., pron.) their, theirs, them
36. y (adv.) there; (pron.) it
37. dire (verb) to say; (noun [m.]) saying
38. elle (pron.) she, her
39. devoir (verb) to have to, owe; (noun [m.]) duty
40. avant (prep., adv.) before; (noun [m.]) front
41. deux (det., noun [m.]) two
42. même (adj., pron.) same; (adv.) even
43. prendre (verb) to take
44. aussi (adv.) to, also; (conj.) as
45. celui (pron.) that, the one, he, him
46. donner (verb) to give
47. bien (adv.) well; (noun [m.]) good
48. où (adv., pron.) where
49. fois (noun [f.]) time(s)
50. vous (pron.) you
51. encore (adv.) again, yet
52. nouveau (adj.) new; (noun [m.]) new (thing)
53. aller (verb) to go
54. cela (pron.) that, it
55. entre (prep.) between
56. premier (det., adj.) first
57. vouloir (verb) to want; (noun [m.]) will, desire
58. déjà (adv.) already
59. grand (adj., adv.) great, big, tall
60. mon (det.) my
61. me (pron.) me, to me, myself
62. moins (adv.) less; (prep., noun [m.]) minus
63. aucun (det., adj., pron.) none, either, neither, not any
64. lui (pron.) him, her
65. temps (noun [m.]) time
66. très (adv.) very
67. savoir (verb) to know; (noun [m.]) learning, knowledge
68. falloir (verb) to take, require, need
69. voir (verb) to see
70. quelque (det., adj., adv.) some
71. sans (prep.) without
72. raison (noun [f.]) reason
73. notre (det.) our
74. dont (pron.) whose, of which
75. non (adv.) no, not
76. an (noun [m.]) year
77. monde (noun [m.]) world, people
78. jour (noun [m.]) day
79. monsieur (noun [m.]) mister, sir, gentleman
80. demander (verb) to ask for
81. alors (adv.) then, so
82. après (adv., prep.) after
83. trouver (verb) to find
84. personne (noun [f.]) person; (pron.) anyone, nobody
85. rendre (verb) to render, return, yield, give up
86. part (noun [f.]) share
87. dernier (adj). last
88. venir (verb) to come
89. pendant (adj.) during; (prep.) for; (noun [m.]) pendant
90. passer (verb) to pass
91. peu (adv.) little
92. lequel (pron.) who, whom, which
93. suite (noun [f.]) result, follow-up, rest
94. bon (adj., adv.) good; (noun [m.]) coupon, voucher
95. comprendre (verb) to understand
96. depuis (prep., adv.) since
97. point (adv.) at all; (noun [m.]) point
98. ainsi (adv.) thus
99. heure (noun [f.]) hour
100. rester (verb) to stay1. être to be
2. avoir to have
3. pouvoir can, to be able
4. faire to do, make
5. mettre to put, place
6. dire to say
7. devoir to have to, owe
8. prendre to take
9. donner to give
10. aller to go
11. vouloir to want
12. savoir to know
13. falloir to take, require, need
14. voir to see
15. demander to ask for
16. trouver to find
17. rendre to render, return, yield, give up
18. venir to come
19. passer to pass
20. comprendre to understand
21. rester to stay
22. tenir to hold
23. porter to wear, carry
24. parler to speak
25. montrer to show1. un a, an, one
2. sur sour (on, upon)
3. leur their (theirs, them)
4. avant before
5. même same
6. bien well
7. nouveau new
8. moins less
9. aucun none, either, neither, not any
10. quelque some
11. pendant during
12. bon bon
13. seul alone, only
14. fort strong
15. certain certain, sure
16. fin fine
17. enfant child
18. fait done, fact
19. tel such
20. droit right
21. quel which, what
22. chaque each
23. possible possible
24. moyen medium
25. plusieurs several1. ne not
2. pas not
3. plus then
4. tout there
5. mais still, yet
6. comme so, therefore
7. si only
8. y already
9. avant more
10. même same, even, self
11. aussi too, also, as
12. bien well
13. où where
14. encore again, yet
15. déjà already
16. grand great, big, tall
17. moins less
18. très very
19. quelque some
20. non no, not
21. alors then, so
22. après after
23. peu little
24. bon good
25. depuis since, for1. et and
2. que that, which, who, whom
3. mais but
4. comme like, as
5. ou or
6. si if, whether
7. aussi too, also, as
8. quand when
9. donc so, then, therefore, thus
10. soit either ... or
11. car because
12. pourquoi why
13. ni nor
14. comment how
15. lorsque when
16. or now
17. cependant however
18. puisque since
19. toutefois however
20. combien how much, how many
21. sinon otherwise, or else
22. néanmoins nevertheless
23. quoique although, though1. de of, from, some, any
2. à to, at, in
3. en in, by
4. pour for, in order to
5. dans in, into, from
6. sur on, upon
7. par by
8. avec with
9. avant before
10. entre between
11. moins less
12. sans without
13. après after
14. pendant during
15. depuis since, for
16. contre against
17. sous under
18. jusque to, up to, until
19. vers toward
20. dès from, as soon
21. devant in front, ahead
22. chez at, with
23. près near, nearby, close by
24. selon according to
25. parmi among1. le him, her, it, them
2. un a, an, one
3. en in, by
4. que that, which, who, whom
5. ce this, that
6. il he, it
7. qui who, whom
8. se oneself, himself, herself, itself, themselves
9. je I
10. tout all
11. autre other
12. on one, we
13. nous we, us
14. leur them, their, theirs
15. y there
16. elle she, her
17. même same, even, self
18. celui that, the one, he, him
19. où where
20. vous you
21. cela that, it
22. me me, to me, myself
23. aucun none, either, neither, not any
24. lui him, her
25. dont whose, of which1. le the
2. de some, any
3. un a, an, one
4. ce this, that
5. tout all, very
6. son his, her, its
7. autre other
8. leur them, their, theirs
9. deux two
10. premier first
11. mon my
12. aucun none, either, neither, not any
13. quelque some
14. notre our
15. certain certain
16. trois three
17. tel such
18. quel which, what
19. chaque each
20. plusieurs several
21. votre your
22. quatre four
23. cinq five
24. ton your
25. dix ten1. être (m.) being
2. avoir (m.) possession
3. pas (m.) footstep
4. pouvoir (m.) power
5. son (m.) sound, bran
6. dire (m.) saying
7. devoir (m.) duty
8. avant (m.) front
9. deux (m.) two
10. bien (m.) good
11. fois (f.) time, times
12. nouveau (m.) new (thing)
13. vouloir (m.) desire
14. moins (m.) minus
15. temps (m.) time, times
16. savoir (m.) knowledge
17. raison (f.) reason
18. non (m.) no
19. an (m.) year
20. monde (m.) world, people
21. jour (m.) day
22. monsieur (m.) mister, sir, gentleman
23. personne (f.) person, people, anyone, nobody
24. part (f.) share
25. pendant (m.) perndant展开阅读
Cc(Coucou) = Hello
Cv(ça va?) = OK?
Svp(S'il vous plaît) = Please
bcp = beaucoup
en PV(privée) = 私聊 例句:Passe en Pv là ce sera mieux
q(que) = that
d(de) = to
m(me) = me
cqe = ce que
paf = 砰
se faire avoir = get fucked up
merci quand même = thanks anyway
ce serait plus que gentil de ta part = it will be more than nice of you
fap = 撸(拟声词)
展开阅读
在学习法语的过程中,学习词汇的顺序很重要。学习词汇的顺序应为从高频词汇到低频词汇。因此有必要统计出最常见的法语高频核心词汇以加速法语词汇学习。
使用NLTK的nltk.probability.FreqDist()可以方便地获得排序后的词频统计结果
from nltk.stem.wordnet import WordNetLemmatizer
from nltk.probability import FreqDist
from nltk import RegexpTokenizer
toknizer = RegexpTokenizer(r'''\w'|\w+|[^\w\s]''')
def get_top_words(path, coding):
f = open(path,encoding=coding)
text = f.read().lower()
f.close()
words = toknizer.tokenize(text)
words = [WordNetLemmatizer().lemmatize(word) for word in words]
fdist = FreqDist(words)
tops = fdist.most_common(len(fdist))
return tops
tops = get_top_words('corpus.txt','utf8')
topf = open('list.txt','w',encoding='utf8')
for j in tops:
i = j[0]
if all((char>='a' and char<='z') or (char>='A' and char<='Z') or (char>='Ï' and char<='œ') for char in i):
topf.write(i)
topf.write('\n')
topf.close()使用Dragon Age Inquisition解包后的游戏内文本作为语料库,得到如下常用法语词汇:
de:从……,……的,以……,
le:定冠词
la:定冠词
vous:你们,您
à:(介词prép)表方向,表目的,表给予,表状况,表工具,表方式,表归属
et:和,而且
que:(关系代词pron.rel)那个, (疑问代词pron.interrog)什么
que:(连词conj.)引出从句,引导独立句表愿望,=pourquoi/si ce n'est/comme/quand/puisque/si,作为tel/quel/même和比较级的关联词
que: (副词adv.)多么
est:是,存在
il:他
je:我
un:一个
pa=pas:(阳性名词n.m.)步,(副词)表否定
en: (人称代词)=de lui/d'elle/d'eux/d'elles/de cela,(介词)在……内,(副词)从……那里
ce: (指示代词)这
une: 一个
ne:不
pour:(介词)为了,去,对于,以为,如此……以至于,因为
qu'=que
nous: 我们
qui: (关系代词)那个人,那些人,任何人,(疑问代词)谁,不管是谁
dans: (介词)在……里,在……时,在……后
ou: 在哪里,(关系副词),在……时
on: 某人,人们,大家
mais: (连词)可是
plus: (副词)更多
sur: (介词)在……上面,向着,关于,根据,通过,在……中,将近,处于……情况
tout: 整个的,所有的,任何,大家,一切
votre: 你们的,您的
si: 如果,只要
s' = se
par: 通过,因为,用,
me: (直接宾语)我,(间接宾语)对我,(自反人称代词)自己
se: 自己
elle: 她
sont:是
être:是
bien:好,很
ont: 有(avoir的一般现在时)
avec: 和……一起,用,对于,带有,尽管
y : there, it
avez: 有
peut:能(pouvoir的第三人称单数变位)
aux=à+les
au=à+le
du=de+le
des=de+les
comme: 好像,简直,作为,当……时,由于
font: 做(faire一般现在时)
moi: 我
était: (他)是(être未完成过去时变位)
son: 他的
leur: 他们的
fait: 事实,行动,现象
faire: 做
ce, cet: 这(阳性单数)
cette: 这(阴性单数)
ces: 这(阳阴性复数)
suis: (我)是(être变位)
non: (副词)不,不是
ma: 我的(阴性)
même: 同样的,自己
notre: 我们的(阳性)
sa: 他们的(阴性)
été: 是(être复合过去式)
vos: 你们的(votre变位)
mon: 我们的(阳性)
lui: 他(宾语)
êtes: (你们)是(être变位)
tous: 全部的,一切(阳性复数)
toute: 全部的,一切(阴性单数)
toutes: 全部的,一切(阴性复数)
t' = tu,你
autres: 另外的,又一个,不一样的(复数)
là: 那里
ici: 这里
sans: 没有,否则
quand: 当……的时候
autre: 另外一个的
rien: 什么都没有
jamais: 从来没有
où: 哪里,在……时候
va: 行,好
quoi: 什么,无论什么
soit: 即,假设有,好吧
aussi: 也
avoir: 有
dit: (他,她)说(dire变位)
leurs: 他们的
monde: 世界
toujours: 总是
encore: 还,又,再
dire: 说
avant: 在……之前
après: 在……之后
c' = ce
avait: (他,她)有(avoire未完成过去时)
peu: 少
quelque: 某个,几个,……多,大约
données: 数据(复数)
alors: 那时
vie: 生活
besoin: 需要
deux: 两个
comment: 怎么
voir: 看见
oui: 是
pourquoi: 为什么
fois: 次
faut: (我)需要(falloir变位)
maintenant: 现在
entre: 在……之间
mieux: 更好
trop: 太
bon: 好(阳性)
moins: 少
très: 很
vu: 看见(voir复合过去时)
grand: 大
sou: 钱
vraiment: 真的
compte: 计算
contre: 挨着
sais: (我,你)知道(savoir变位)
fort: 强大的
personne: 人
faites: (你们)做(faire变位)
ca
d' = de
peux: (我,你)能(pouvoir动词变位)
donc: 因此
eux: 他们
ceux: 这个,这些(复数)
tu: 你
展开阅读
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<ctime>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
string type2str(int type) {
string r;
uchar depth = type & CV_MAT_DEPTH_MASK;
uchar chans = 1 + (type >> CV_CN_SHIFT);
switch (depth) {
case CV_8U: r = "8U"; break;
case CV_8S: r = "8S"; break;
case CV_16U: r = "16U"; break;
case CV_16S: r = "16S"; break;
case CV_32S: r = "32S"; break;
case CV_32F: r = "32F"; break;
case CV_64F: r = "64F"; break;
default: r = "User"; break;
}
r += "C";
r += (chans + '0');
return r;
}
bool isU(int type) {
string r;
uchar depth = type & CV_MAT_DEPTH_MASK;
uchar chans = 1 + (type >> CV_CN_SHIFT);
switch (depth) {
case CV_8U: return true; break;
case CV_8S: return false; break;
case CV_16U: return true; break;
case CV_16S: return false; break;
case CV_32S: return false; break;
case CV_32F: return false; break;
case CV_64F: return false; break;
default: return false; break;
}
}
bool isF(int type) {
string r;
uchar depth = type & CV_MAT_DEPTH_MASK;
uchar chans = 1 + (type >> CV_CN_SHIFT);
switch (depth) {
case CV_8U: return false; break;
case CV_8S: return false; break;
case CV_16U: return false; break;
case CV_16S: return false; break;
case CV_32S: return false; break;
case CV_32F: return true; break;
case CV_64F: return true; break;
default: return false; break;
}
}
Mat U2F(Mat src)
{
// convert unsigned char (0-255) image to float (0-1) image
Mat dst;
src.convertTo(dst, CV_32F, 1 / 255.0);
return dst;
}
Mat F2U(Mat src)
{
// convert float (0-1) image to unsigned char (0-255) image
Mat dst = src.clone()*255;
src.convertTo(dst, CV_8U, 1);
return dst;
}
void print_size(Mat src)
{
// print height width channels
int size_h = src.size[0];
int size_w = src.size[1];
int size_z = src.channels();
cout << type2str(src.type()) << endl;
cout << "h: " << size_h << " w: " << size_w << " z: " << size_z << endl;
return;
}
double min(Mat Y)
{
// return min element in an image
double min, max;
minMaxIdx(Y, &min, &max);
return min;
}
double max(Mat Y)
{
// return max element in an image
double min, max;
minMaxIdx(Y, &min, &max);
return max;
}
void arg_min(Mat Y, int idx[2])
{
minMaxIdx(Y, 0, 0, idx, 0);
return;
}
void arg_max(Mat Y, int idx[2])
{
minMaxIdx(Y, 0, 0, 0, idx);
return;
}
Mat reduce_min(Mat in)
{
Mat src = in.clone();
// reduce min of an image over the third dimension
int size_h = src.size[0];
int size_w = src.size[1];
int size_z = src.channels();
vector<Mat> channels(size_z);
split(src, channels);
Mat minmat;
if (isF(src.type()))
{
minmat = Mat(size_h, size_w, CV_32F, Scalar(FLT_MAX));
}
else if (isU(src.type()))
{
minmat = Mat(size_h, size_w, CV_8U, Scalar(255));
}
for (int z = 0; z < size_z; ++z)
{
min(channels[z], minmat, minmat);
}
return minmat;
}
Mat reduce_max(Mat in)
{
Mat src = in.clone();
// reduce max of an image over the third dimension
int size_h = src.size[0];
int size_w = src.size[1];
int size_z = src.channels();
vector<Mat> channels(size_z);
split(src, channels);
Mat maxmat;
if (isF(src.type()))
{
maxmat = Mat(size_h, size_w, CV_32F, Scalar(FLT_MIN));
}
else if (isU(src.type()))
{
maxmat = Mat(size_h, size_w, CV_8U, Scalar(0));
}
for (int z = 0; z < size_z; ++z)
{
max(channels[z], maxmat, maxmat);
}
return maxmat;
}
Mat reduce_mean(Mat in)
{
Mat src = in.clone();
if (!isF(src.type()))
{
src = U2F(src);
}
// reduce mean of an image over the third dimension
int size_h = src.size[0];
int size_w = src.size[1];
int size_z = src.channels();
vector<Mat> channels(size_z);
split(src, channels);
Mat summat(size_h, size_w, CV_32F, Scalar(0));
for (int z = 0; z < size_z; ++z)
{
summat = summat + channels[z];
}
return summat/size_z;
}
Mat cumsum(Mat src)
{
Mat dst = src.clone();
if (!isF(dst.type()))
{
dst = U2F(dst);
}
// cumsum of Mat array
int size_h = dst.size[0];
int size_w = dst.size[1];
for (int i = 1; i < size_h; ++i)
{
dst.at<float>(i) += dst.at<float>(i - 1);
}
return dst;
}
template<typename T>
vector<float> cumsum_vec(vector<T> src)
{
vector<float> dst(src.size(), 0);
for (int i = 0; i < src.size(); ++i)
{
dst[i] = (float)src[i];
}
for (int i = 1; i < src.size(); ++i)
{
dst[i] += dst[i - 1];
}
return dst;
}
Mat myCalcHist(Mat V1, int bins = 100)
{
Mat ht;
int channels[] = { 0 };
int histSize[] = { bins };
float granges[] = { 0, 255 };
const float* ranges[] = { granges };
calcHist(&V1, 1, channels, Mat(), ht, 1, histSize, ranges, true, false);
return ht;
}
bool all(Mat src)
{
int size_h = src.size[0];
int size_w = src.size[1];
int size_z = src.channels();
bool result = true;
for (int i = 0; i < size_h; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < size_w; j++)
{
for (int z = 0; z < size_z; z++)
{
if (src.at<uchar>(i,j,z) == 0)
result = false;
}
}
}
return result;
}
template<typename T>
vector<T> abs(vector<T> src)
{
vector<T> dst(src.begin(), src.end());
for (int i = 0; i < src.size(); i++)
{
dst[i] = abs(src[i]);
}
return dst;
}
bool all(vector<bool> mask)
{
bool result = true;
for (int i = 0; i < mask.size(); i++)
{
if (!mask[i])
result = false;
}
return result;
}
Mat masked_array(Mat src, Mat mask, int padd=255)
{
int size_h = src.size[0];
int size_w = src.size[1];
int size_z = src.channels();
Mat result = src.clone();
for (int i = 0; i < size_h; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < size_w; j++)
{
for (int z = 0; z < size_z; z++)
{
if (!(mask.at<uchar>(i, j, z) == 0))
{
result.at<int>(i, j, z) = padd;
}
else
{
result.at<int>(i, j, z) = src.at<int>(i, j, z);
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
template<typename T>
vector<T> masked_array(vector<T> src, vector<bool> mask, T padd)
{
vector<T> result(src.size(), padd);
for (int i = 0; i < src.size(); i++)
{
if (!(mask[i] == false))
{
result[i] = padd;
}
else
{
result[i] = src[i];
}
}
return result;
}
template <typename T, typename Compare>
std::vector<std::size_t> sort_permutation(
const std::vector<T>& vec,
Compare& compare)
{
std::vector<std::size_t> p(vec.size());
std::iota(p.begin(), p.end(), 0);
std::sort(p.begin(), p.end(),
[&](std::size_t i, std::size_t j){ return compare(vec[i], vec[j]); });
return p;
}
template <typename T>
std::vector<T> apply_permutation(
const std::vector<T>& vec,
const std::vector<std::size_t>& p)
{
std::vector<T> sorted_vec(vec.size());
std::transform(p.begin(), p.end(), sorted_vec.begin(),
[&](std::size_t i){ return vec[i]; });
return sorted_vec;
}
void unique(vector<int> src, vector<int>& uni, vector<int>& idx, vector<int>& count)
{
idx = vector<int>(src.size(), 0);
int hash[256] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < src.size(); i++)
{
hash[src[i]]++;
}
int k = 0;
int new_idx[256];
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
if (hash[i] != 0)
{
uni.push_back(i);
count.push_back(hash[i]);
new_idx[i] = k;
k++;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < src.size(); i++)
{
idx[i] = new_idx[src[i]];
}
return;
}
template<typename T>
void print(std::vector <T> const &a) {
std::cout << "The vector elements are : ";
for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++)
std::cout << a.at(i) << ' ';
std::cout << "\n" << endl;
}
template<typename T>
std::vector<T> slice_vec(std::vector<T> const &v, int m, int n)
{
auto first = v.cbegin() + m;
auto last = v.cbegin() + n + 1;
std::vector<T> vec(first, last);
return vec;
}
Mat zmMinFilterGray(Mat src, int r = 7)
{
Mat dst;
erode(src, dst, getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size(2 * r + 1, 2 * r + 1)));
//imshow("erode", dst);
waitKey();
return dst;
}
Mat guidedfilter(Mat I, Mat p, int r, float eps)
{
Mat m_I, m_p, m_Ip, m_II, m_a, m_b;
boxFilter(I, m_I, -1, { r, r });
boxFilter(p, m_p, -1, { r, r });
boxFilter(I.mul(p), m_Ip, -1, { r, r });
Mat cov_Ip = m_Ip - m_I.mul(m_p);
boxFilter(I.mul(I), m_II, -1, { r, r });
Mat var_I = m_II - m_I.mul(m_I);
Mat a = cov_Ip / (var_I + eps);
Mat b = m_p - a.mul(m_I);
boxFilter(a, m_a, -1, { r, r });
boxFilter(b, m_b, -1, { r, r });
return m_a.mul(I) + m_b;
}
int getV1(Mat m, int r, float eps, float w, float maxV1, Mat &V1, float& A)
{
Mat ht;
V1 = reduce_min(m);
//imshow("dark", V1);
waitKey();
V1 = guidedfilter(V1, zmMinFilterGray(V1, 7), r, eps);
//imshow("filter", V1);
waitKey();
int bins = 100;
int channels[] = { 0};
int histSize[] = { bins };
float granges[] = { 0, 1 };
const float* ranges[] = { granges };
calcHist(&V1, 1, channels, Mat(), ht, 1, histSize, ranges, true, false);
ht.convertTo(ht, CV_32F, V1.size[0] * V1.size[1]);
Mat d = cumsum(ht);
int lmax = bins - 1;
for (; lmax > 0; lmax--)
{
if (d.at<float>(lmax) < 0.999)
break;
}
Mat avg = reduce_mean(m);
int size_h = m.size[0];
int size_w = m.size[1];
//cout << "lmax" << lmax << endl;
A = -1; //negative inf
for (int i = 0; i < size_h; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < size_w; ++j)
{
if (V1.at<float>(i, j) >= lmax / bins)
if (avg.at<float>(i, j)>A)
A = avg.at<float>(i, j);
}
}
min(V1*w, maxV1, V1);
return 0;
}
Mat deHaze(Mat m, int r = 81, float eps = 0.001, float w = 0.95, float maxV1 = 0.80)
{
m = U2F(m);
int size_h = m.size[0];
int size_w = m.size[1];
int size_z = m.channels();
Mat Y = m.clone();
Mat V1;
float A;
getV1(m, r, eps, w, maxV1, V1, A);
//imshow("V1", V1);
waitKey(0);
vector<Mat> channels_Y(size_z);
vector<Mat> channels_m(size_z);
//split(Y, channels_Y);
split(m, channels_m);
//cout << "A" << A << endl;
for (int k = 0; k < size_z; ++k)
{
channels_Y[k] = (channels_m[k] - V1) / (1 - V1 / A);
}
merge(channels_Y, Y);
max(Y, 0, Y); //clip
min(Y, 1, Y); //clip
Y = 255 * Y;
Y = F2U(Y);
return Y;
}
void normalize(Mat &src)
{
src.convertTo(src, CV_32F, 1.0/max(src));
src.convertTo(src, CV_8U, 255);
}
template<typename T>
int find_nearest_above(vector<T> my_array, T target)
{
vector<T> diff(my_array.size(), 0);
for (int i = 0; i < my_array.size(); i++)
{
diff[i] = my_array[i] - target;
}
vector<bool> mask(my_array.size(), false);
for (int i = 0; i < diff.size(); i++)
{
mask[i] = diff[i]<=-1;
}
if (all(mask))
{
vector<T> abs_diff = abs(diff);
vector<T>::iterator iter = min_element(abs_diff.begin(), abs_diff.end());
int c = iter - abs_diff.begin();
return c;
}
vector<T> masked_diff = masked_array(diff, mask, 255);
vector<T>::iterator iter = min_element(masked_diff.begin(), masked_diff.end());
int c = iter - masked_diff.begin();
return c;
}
Mat hist_match(Mat original, Mat specified)
{
int ori_h = original.size[0];
int ori_w = original.size[1];
int sp_h = specified.size[0];
int sp_w = specified.size[1];
vector<int> ori_array(ori_h*ori_w, 0), sp_array(sp_h*sp_w,0);
for (int i = 0; i < ori_h; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < ori_w; j++)
{
ori_array[i*ori_w + j] = original.at<uchar>(i, j);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < sp_h; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < sp_w; j++)
{
sp_array[i*sp_w + j] = specified.at<uchar>(i, j);
}
}
vector<int> s_values, bin_idx, s_counts, t_values, t_counts;
unique(ori_array, s_values, bin_idx, s_counts);
unique(sp_array, t_values, vector<int>(), t_counts);
/*print(s_values);
vector<int> sliced = slice_vec(bin_idx, 0, 10);
print(sliced);
print(s_counts);*/
vector<float> s_quantities = cumsum_vec(s_counts);
vector<float> t_quantities = cumsum_vec(t_counts);
for (int i = 0; i < s_quantities.size(); i++)
{
s_quantities[i] /= s_quantities[s_quantities.size()-1];
}
for (int i = 0; i < t_quantities.size(); i++)
{
t_quantities[i] /= t_quantities[t_quantities.size() - 1];
}
vector<int> sour(s_quantities.size(), 0), temp(t_quantities.size(), 0);
for (int i = 0; i < s_quantities.size(); i++)
{
sour[i] = (int)(s_quantities[i] * 255);
}
for (int i = 0; i < t_quantities.size(); i++)
{
temp[i] = (int)(t_quantities[i] * 255);
}
vector<int> b;
for (int i = 0; i < sour.size(); i++)
{
b.push_back(find_nearest_above(temp, sour[i]));
}
/*cout << "b[i]" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < b.size(); i++)
{
cout << b[i] << endl;
}*/
Mat dst = original.clone();
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < ori_h; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < ori_w; j++)
{
dst.at<uchar>(i, j) = b[bin_idx[k]];
k++;
}
}
return dst;
}
Mat bright_hist_match(Mat src)
{
if (!isU(src.type()))
{
src = F2U(src);
}
int size_h = src.size[0];
int size_w = src.size[1];
int size_z = src.channels();
Mat dst;
Mat equalized;
vector<Mat> channels_src(size_z);
vector<Mat> channels_tmp(size_z);
vector<Mat> channels_dst(size_z);
split(src, channels_src);
for (int i = 0; i < size_z; i++)
{
equalizeHist(channels_src[i], channels_tmp[i]);
}
merge(channels_tmp, equalized);
Mat bright_prior = reduce_max(equalized);
for (int i = 0; i < size_z; i++)
{
channels_dst[i] = hist_match(channels_tmp[i], bright_prior);
}
merge(channels_dst, dst);
print_size(dst);
normalize(dst);
return dst;
}
int main()
{
clock_t start, end;
Mat img = imread("100.png");
start = clock();
img = deHaze(img);
end = clock();
double cost = (double)(end - start)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
//cout.setf(ios::fixed);
cout << "使用时间:" << cost << "s" << endl;
cout << "分辨率:" << img.size[1] << "x" << img.size[0] << endl;
imshow("fuck",img);
waitKey(0);
}